TradingView India: How to Use It for Stock Chart Analysis
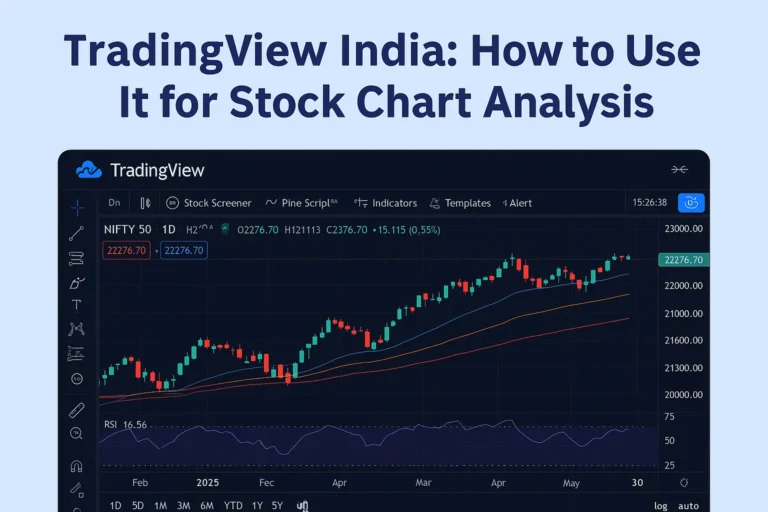
TradingView is one of the most popular charting platforms used by traders and investors around the world. For Indian stock market participants, TradingView India offers an intuitive, web-based interface to analyze charts, apply technical indicators, and track market trends in real-time. This guide explains how to effectively use TradingView India for stock chart analysis. 1….